How the courtroom is set out
How the court is set out may depend on the type of court.
Your Child and Youth Witness Service (CYWS) practitioner can provide details about what the courtroom will look like if you would like to know more.
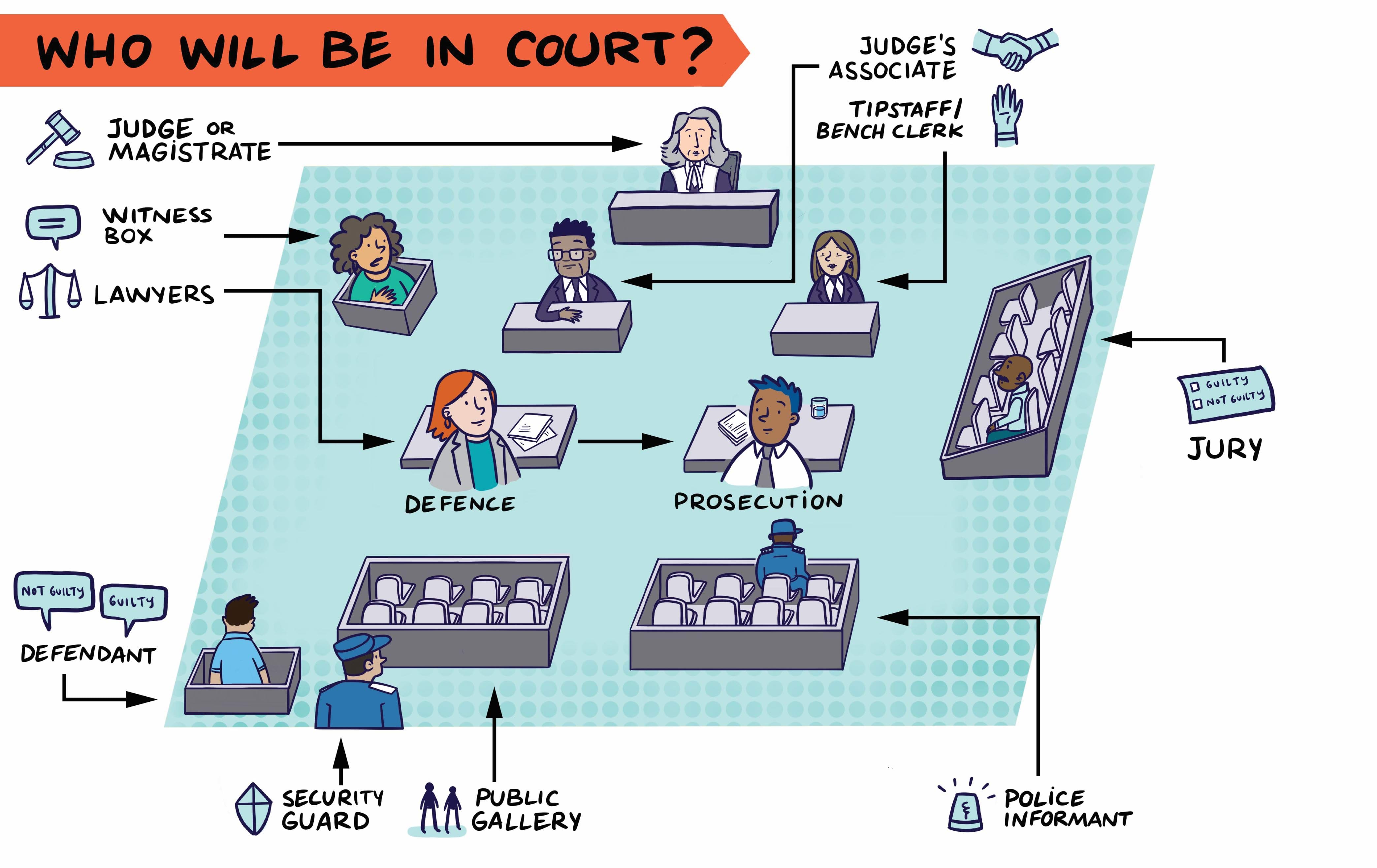
You can download/print this infographic at the end of the page.
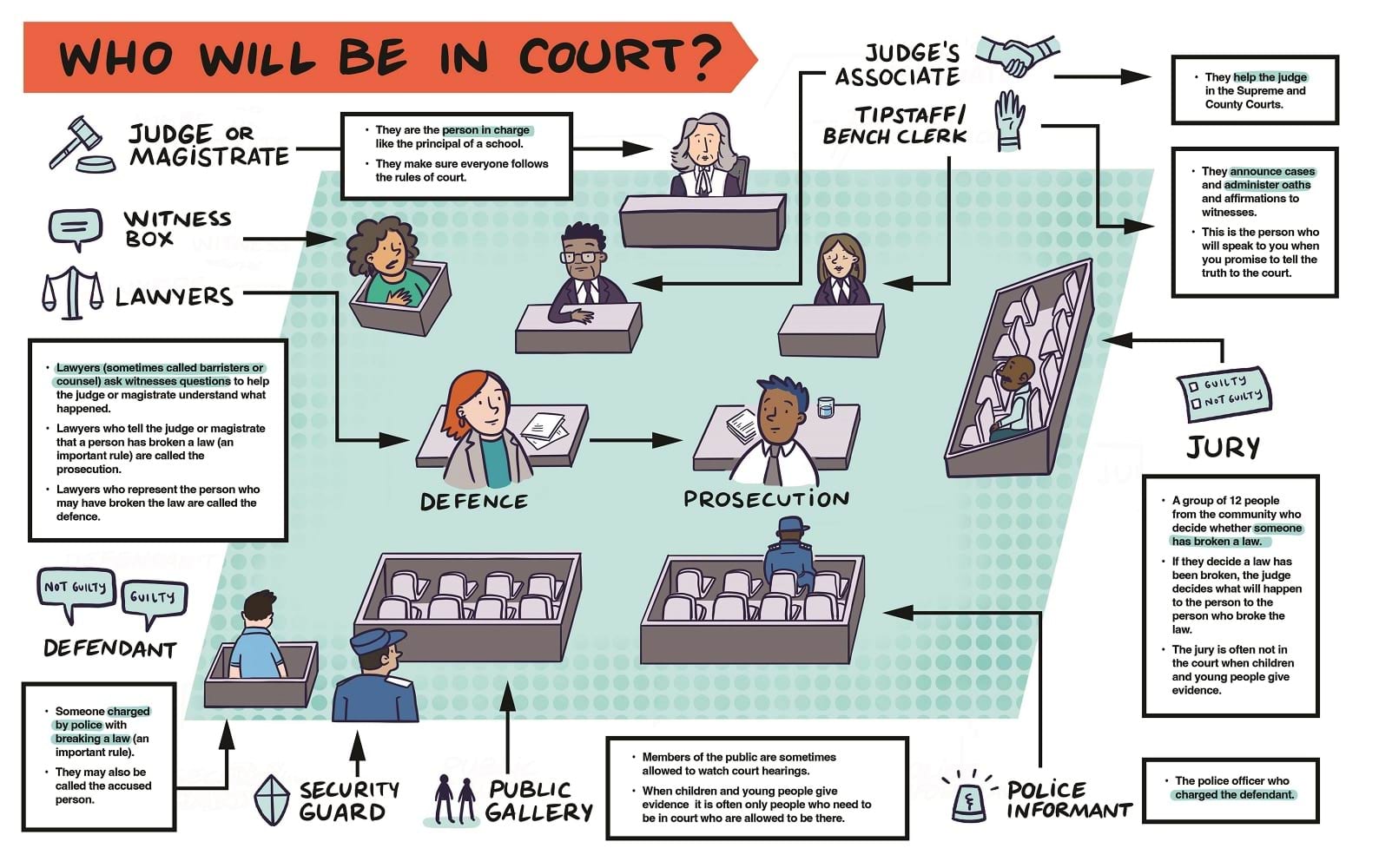
Judge or magistrate
Sits at the front of the court facing the courtroom.
They are the person in charge, like the principal of a school.
They make sure everyone follows the rules of the court.
Judge's associate
Sits near the judge at the front of the courtroom.
They help the judge in the Supreme and County Courts.
Tipstaff/Bench Clerk
You will find a tipstaff in the Supreme and County Courts and a bench clerk in the Children's and Magistrates' Courts. They sit near the judge or magistrate.
They announce cases and administer oaths and affirmations to witnesses.
This is the person who will speak to you when you promise to tell the truth to the court.
Lawyers
Lawyers for the prosecution and defence usually sit near the centre of the courtroom.
Lawyers ask witnesses questions to help the judge or magistrate understand what happened.
The lawyers who tell the judge or magistrate that a person has broken a law (an important rule) are called the prosecution.
The lawyers who represent the person who may have broken the law are called the defence.
Lawyers who ask questions in court are sometimes called barristers or counsel.
Witness box
This is where the witness, usually an adult, will be when they answer questions from lawyers in court (also called 'giving evidence'). The witness box is usually towards one side of the court, near the judge or magistrate.
Children and young people don't usually sit in a witness box because they give evidence away from the court.
Defendant
The defendant is the person who is charged by police with breaking a law (an important rule).
They may also be called the accused person.
The defendant will often sit in a dock at the back of the courtroom. In some cases, they will sit in the public gallery behind the defence lawyers.
Your CYWS practitioner will be able to give you more information about this if you would like to know more.
Security guard
A security guard stands next to the defendant.
Jury
The jury is a group of 12 people from the community who decide whether someone has broken a law (an important rule).
If they decide a law has been broken, the judge decides what will happen to the person who broke the law.
Not all courts have juries and the jury is often not in the court when children and young people give evidence.
Public gallery
Members of the public are sometimes allowed to watch court hearings.
When children and young people give evidence, it is often only people who need to be in court who are allowed to be there.
Police informant
This is the police officer who charged the defendant.
The police informant sits in the public gallery, behind the prosecution.
Infographic for download
Updated